Radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in a straight line (like a 'ray' in geometry'). This line travels through space or some material, spreading out from the source in all directions; "radiating" out. Radiation can also refer to the emitted energy itself. There are many different types of radiation that can include electromagnetic, thermal, acoustic, particle radiation (such as alpha or beta radiation from a radioactive source), and ionizing radiation.
Electromagnetic Radiation
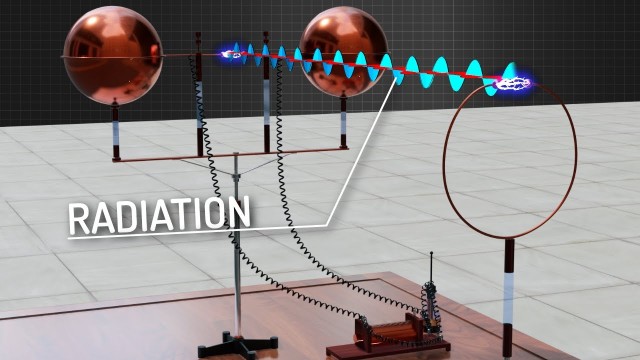
Electromagnetic radiation is produced by accelerating charges and moves through space as with its electric and magnetic fields oscillating. This radiation is also known as an electromagnetic wave as it is composed of alternating electric and magnetic fields. This type of radiation comes in discrete packets known as photons.
There are several different types of electromagnetic radiation, and their properties depend on their energy and wavelength. Some of the different types include radio waves, infrared radiation (felt as heat), microwaves, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, x-rays, gamma rays, and cosmic rays.
Long wavelength electromagnetic radiation (radio to visible light waves) are generally non-ionizing. Shorter wavelength electromagnetic radiation (ultraviolet light to gamma rays) tends to be ionizing.